In 2002, the highest reported efficiency for thin film solar cells based on CdTe is 18%, which was achieved by research at Sheffield Hallam University, although this has not been confirmed by an external test laboratory.
The US national renewable energy research facility NREL achieved an efficiency of 19.9% for the solar cells based on copper indium gallium selenide thin films, also known as CIGS .
NREL has since developed a robot that builds and analyzes the efficiency of thin-film solar cells with the goal of increasing the efficiency by testing the cells in different situations.
These CIGS films have been grown by
Saturday, September 25, 2010
Friday, September 24, 2010
Crystalline silicon
Basic structure of a silicon based solar cell and its working mechanism.
By far, the most prevalent bulk material for solar cells is crystalline silicon (abbreviated as a group as c-Si), also known as "solar grade silicon". Bulk silicon is separated into multiple categories according to crystallinity and crystal size in the resulting ingot, ribbon, or wafer.
- monocrystalline silicon (c-Si): often made using the Czochralski process. Single-crystal wafer cells tend to be expensive, and because they are cut from cylindrical ingots, do not
Thursday, September 23, 2010
Series resistance
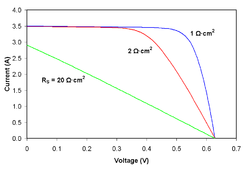
Effect of series resistance on the current-voltage characteristics of a solar cell
As series resistance increases, the voltage drop between the junction voltage and the terminal voltage becomes greater for the same flow of current. The result is that the current-controlled portion of the I-V curve begins to sag toward the origin, producing a significant decrease in the terminal voltage V and a slight reduction in ISC, the short-circuit current. Very high values of RS will also
Wednesday, September 22, 2010
Cell Temperature | Solar Cell

Effect of temperature on the current-voltage characteristics of a solar cell
Temperature affects the characteristic equation in two ways: directly, via T in the exponential term, and indirectly via its effect on I0 (strictly speaking, temperature affects all of the terms, but these two far more significantly than the others). While increasing T reduces the magnitude of the exponent in the characteristic equation, the value of I0 increases exponentially with T. The net effect is to
Tuesday, September 21, 2010
High-efficiency cells
High-efficiency solar cells are a class of solar cell that can generate more electricity per incident solar power unit (watt/watt). Much of the industry is focused on the most cost efficient technologies in terms of cost per generated power.
The two main strategies to bring down the cost of photovoltaic electricity are increasing the efficiency of the cells and decreasing their cost per unit area. However, increasing the efficiency of a solar cell without
The two main strategies to bring down the cost of photovoltaic electricity are increasing the efficiency of the cells and decreasing their cost per unit area. However, increasing the efficiency of a solar cell without
Monday, September 20, 2010
Light-absorbing dyes (DSSC)
Typically a ruthenium metalorganic dye (Ru-centered) is used as a monolayer of light-absorbing material. The dye-sensitized solar cell depends on a mesoporous layer of nanoparticulate titanium dioxide to greatly amplify the surface area (200–300 m2/g TiO2, as compared to approximately 10 m2/g of flat single crystal). The photogenerated electrons from the light absorbing dye are passed on to the n-type TiO2, and the holes are passed to an electrolyte on the
Sunday, September 19, 2010
Concentrating photovoltaics (CPV)
Concentrating photovoltaic systems use a large area of lenses or mirrors to focus sunlight on a small area of photovoltaic cells.High concentration means a hundred or more times direct sunlight is focused when compared with crystalline silicon panels. Most commercial producers are developing systems that concentrate between 400 and 1000 suns.
All concentration systems need a one axis or more often two axis tracking system for high precision, since
All concentration systems need a one axis or more often two axis tracking system for high precision, since
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)